In hazardous work environments where exposure to dangerous substances is a concern, the importance of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) cannot be overstated. PPE serves as a crucial line of defense against potential health risks and injuries. Understanding the significance of PPE and its proper utilization is paramount for ensuring the safety and well-being of workers in various industries.
Understanding Hazardous Materials
Hazardous materials encompass a broad range of substances that pose risks to human health, property, or the environment. These materials can include chemicals, biological agents, radioactive substances, and other potentially harmful elements. Exposure to hazardous materials can result in adverse health effects ranging from skin irritation to respiratory issues and even long-term illnesses.
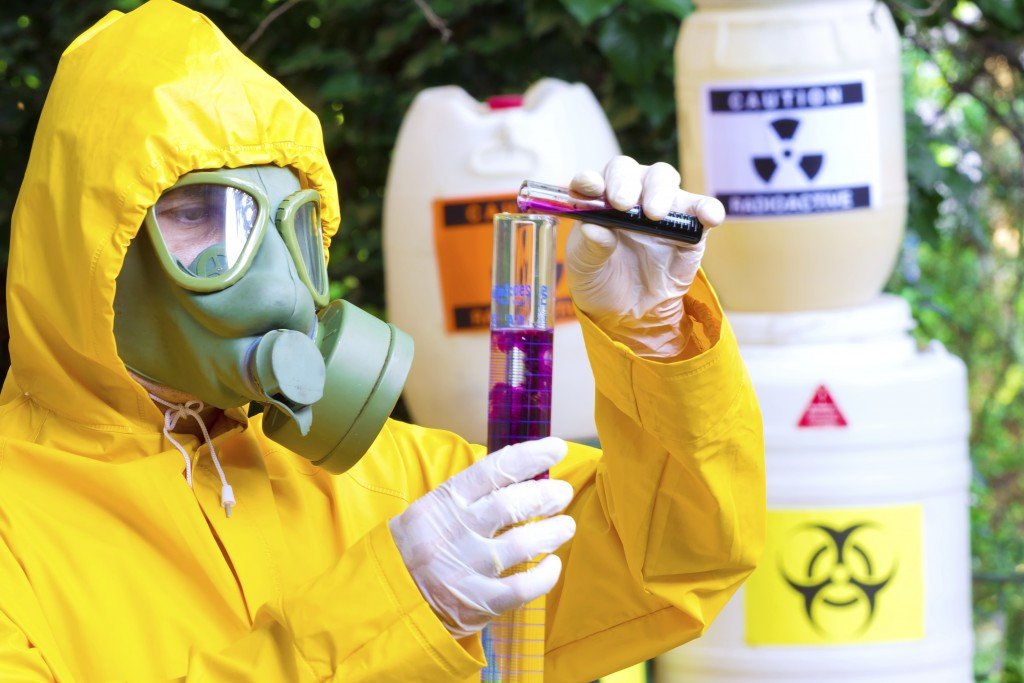

The Role of Personal Protective Equipment
Personal Protective Equipment acts as a shield, providing a layer of defense between individuals and hazardous materials. It serves to minimize the risk of exposure by creating a barrier that prevents contact with harmful substances. Properly selected and worn PPE can significantly reduce the likelihood of injuries and illnesses associated with hazardous materials.
Types of PPE for Hazardous Materials
Protective Clothing:
- Coveralls, aprons, and suits made from specialized materials provide full-body protection against chemical splashes, spills, and contamination.
- Gloves made from various materials such as latex, nitrile, or neoprene shield the hands from direct contact with hazardous substances.
- Respiratory Protection:
- Respirators equipped with filters or cartridges are essential for safeguarding against inhaling airborne contaminants like dust, fumes, gases, and vapors.
- Different types of respirators, including N95 masks, half-face respirators, and powered air-purifying respirators (PAPRs), offer varying levels of respiratory protection.
- Eye and Face Protection:
- Safety goggles or face shields shield the eyes and face from chemical splashes, flying debris, and harmful radiation.
- Welding helmets with appropriate filters protect against intense light and heat generated during welding operations.
- Foot and Leg Protection:
- Safety boots or shoes with steel toes and puncture-resistant soles safeguard the feet from sharp objects, heavy falling objects, and chemical spills.
- Leggings or protective covers provide additional protection against splashes and spills in hazardous environments.
Selecting and Using PPE Effectively
Proper selection and use of PPE are critical to ensuring its effectiveness in mitigating risks associated with hazardous materials. Employers and workers alike must adhere to the following guidelines:
Assessment of Hazards: Conduct a thorough assessment of the workplace to identify potential hazards and determine the appropriate types of PPE required.
Proper Fit and Comfort: PPE should fit properly and comfortably to ensure maximum protection without impeding movement or causing discomfort.
Training and Education: Provide comprehensive training and education to workers on the proper use, maintenance, and limitations of PPE.
<
Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain PPE to ensure it remains in good condition and is capable of providing adequate protection.
Replacement when Necessary: Replace damaged or worn-out PPE promptly to maintain its effectiveness in safeguarding against hazards.
Conclusion
In hazardous work environments where exposure to dangerous substances is a concern, Personal Protective Equipment plays a vital role in ensuring the safety and well-being of workers. By understanding the risks associated with hazardous materials and employing appropriate PPE measures, employers and workers can minimize the likelihood of injuries and illnesses, creating a safer and healthier workplace for all.
Also, Reads More>>>Smooth Sailing